JPA프로젝트를 구글링하다보면 Entity와 DTO를 필드가 거의 똑같은데 나눠서 작성한다.
왜 그렇게 해야할까?
Entity 클래스를 데이터베이스와 맞닿은 핵심 클래스로 Request/Response 클래스로 사용하면 안되기 때문이다.
Entity
builder메서드(참고: 빌더패턴을 사용해야하는 이유)를 통해서 DTO를 entity로 변환할 수 있다.
참고로 @ApiModelProperty는 swagger와 관련된 어노테이션으로 JPA와 관련이 없으므로 무시해도 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @Table(name = "board")
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED) @AllArgsConstructor
@Builder(builderMethodName = "ReviewEntityBuilder")
public class ReviewEntity extends TimeEntity {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "게시글 번호")
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "이메일", example = "example@example.com", required = true)
@Column(name = "email", nullable = false)
private String email;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "게시글내용", example = "심장이 떨렸습니다.", required = true)
@Column(name = "content")
private String content;
public static ReviewEntityBuilder builder(ReviewDto dto) {
return ReviewEntityBuilder()
.id(dto.getId())
.email(dto.getEmail())
.content(dto.getContent());
}
}
|
Dto
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class ReviewDto {
private Long id;
private String email;
private String content;
}
|
컨트롤러에서는 뭘 받아야할까? DTO? ENTITY?
컨트롤러에선 DTO로 받아야하며 서비스단에서 ENTITY로 변환 후 DB에 전달하면 된다.
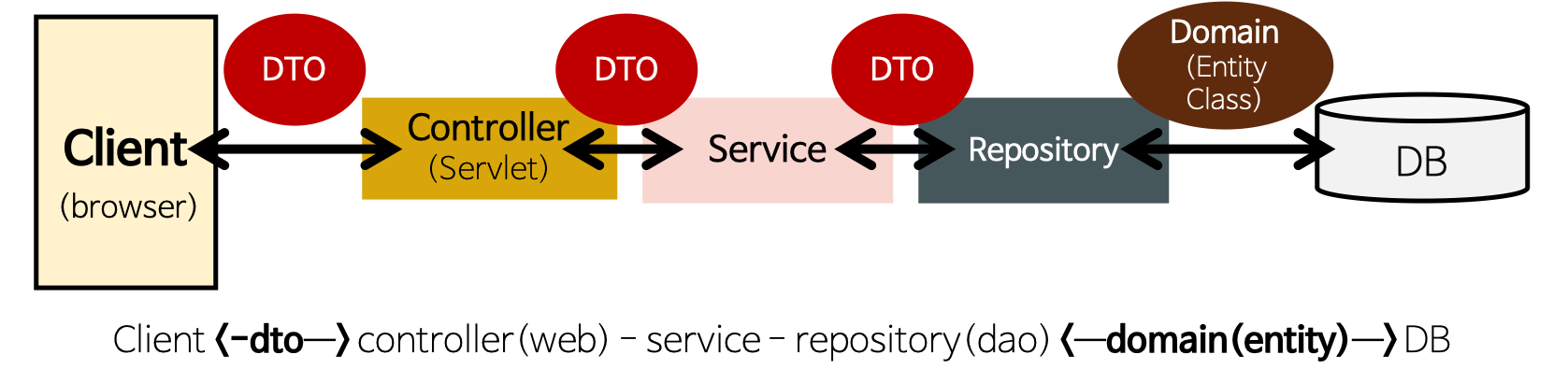
Entity 클래스와 DTO 클래스를 분리하는 이유
- View Layer와 DB Layer의 역할을 철저하게 분리하기 위해
실무에서 서비스가 요청을 처리하고 클라이언트로 반환할때 모델(model) 자체를 그대로 리턴하는 경우는 별로 없고 DTO로 대부분 변환한다.
why?
- 비즈니스 로직 캡슐화를 위해: 보통 모델은 DB테이블구조와 비슷해서 외부인에게 노출되길 원치않음
- 쿨라이언트에게 필요한 정보를 모델이 다 가지고 있지 않아서: ex)에러메시지
참고

![[OS/WINDOW]배포후 서버재시작에 batch와 윈도우 스케줄러 활용하기](https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2012/03/04/00/50/board-22098_960_720.jpg)
![[블로그]헥소테마에서 댓글기능 facebook에서 utterances로 변경하기](https://miro.medium.com/max/1600/1*aOv6h3h_v9PQWa03zGACnw.png)